| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- Python
- kubernetes
- docker
- CVAT
- MAC address
- OS
- Operating System
- AWS
- helm
- grafana
- JavaScript
- ip
- kubeadm
- kubectl
- Packet
- jvm
- zookeeper
- tcp
- log
- PostgreSQL
- Spring
- CSV
- Kafka
- airflow
- java
- Network
- Trino
- EC2
- aws s3
- Vision
- Today
- Total
JUST WRITE
The law of Demeter 본문

The Law of Demeter
Loosely Coupled
객체 지향 디자인에서 결합 정도는 하나의 Class가 다른 Class의 설계에 얼마나 영향을 미치는가이다.
다른 말로 한 Class의 변경으로 다른 Class도 얼마나 자주 변경되는가이다.
Tight Coupling은 두 Class가 함께 변경되는 경우가 많다는 것이고,
Loosely Coupling은 대부분 독립적이다.
일반적으로 테스트, 유지보수 측면에서 유리한 Loosely Coupling을 추천한다.
The Law of Demeter
디미터의 법칙은 Object-oriented programing: an objective sense of style에서 처음 소개되었다.
디미터의 법칙을 한마디로 말하면,,,
Don't talk to starnagers
낮선 이에게 말하지 마라
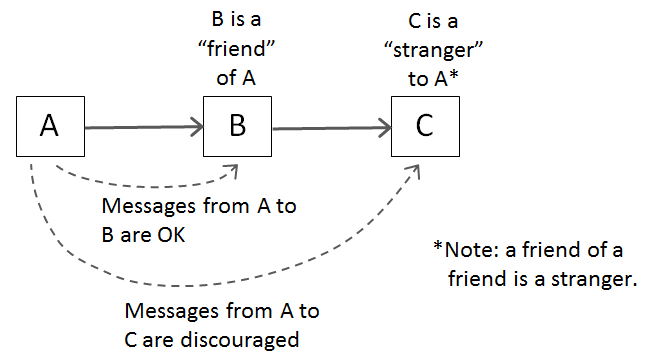
위 그림에서 A Class는 B Class와 친구이다.
A Class는 B Class에게 message를 보낼 수도 있고 받을 수도 있다.
message를 통해 해당 Class에 접근하는 것이다.
C Class는 A Class에게 낮선 존재이다.
A Class가 C Class에게 message를 보내는 것은 바람직하지 못하다.
// 디미터의 법칙 준수
objectA.getObjectB().doSomething();
// 디미터의 법칙 어김.
objectA.getObjectB().getObjectC().doSomething();디미터의 법칙은 제 3의 객체의 메소드에 접근하기 위해 객체에 접근하는 것을 방지하는 것이다.
한 객체가 알아야 하는 다른 객체를 최소한으로 유지하라는 의미로 최소지식원칙이라고도 한다.
상세하게 보면, function은 오직 아래와 같은 Class나 Object에 접근해야 한다.
- Objects in class parameter
- The Object in function parameter
- The Object in class members
- Objects created in function body
아래 코드를 살펴보자.
// Dictionary v1.0
class Dictionary {
Language language;
public String translate (String s) {
return s;
}
}
class Translation {
Dictionary dictionary;
public String translate (String s) {
return dictionary.translate(s);
}
}
// 디미터의 법칙 어긴 사례
public String wrongUsage(Translation translation, String s) {
translation.dictionary.translate(s);
}wrongUsage 메소드에서 Paramter로 넘어온 Translation 객체에서 Dictionary 객체의 메소드를 호출하고 있다.
이거는 디미터의 법칙을 어긴 것이다.
이렇게 디미터의 법칙을 어기면 유지보수가 어렵게 된다.
예로 Dictionary Class의 translate 메소드를 수정하면
// Dictionary v2.0
class Dictionary {
Language language;
public String translate (TranslateString translateString) {
return translateString.toString();
}
}
// Translation v2.0
class Translation {
Dictionary dictionary;
public String translate (String s) {
TranslateString translateString = new TranslateString(s, "someMetadata");
return dictionary.translate(translateString);
}
}
// 기존 wrongUage
// Dictionary, Translation이 수정되면서 Error 발생
public String wrongUsage(Translation translation, String s) {
translation.dictionary.translate(s);
}
// 디미터의 법칙을 지키도록 변경
public String wrongUsage(Translation translation, String s) {
translation.translate(s);
}Dictionary Class 변경되면서 Translation Class도 변경되었다.
Translation 객체를 이용하던 wrongUsage 메소드는 Error가 발생하게 되었다.
아래에 디미터의 법칙을 준수하도록 변경해보았다.
'Programing' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Library vs Framework (0) | 2021.10.09 |
|---|

